What a Good Debt to Asset Ratio Is and How to Calculate It
- Posted on 14 de março de 2024
- in Bookkeeping
- by admin

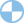
For companies with low debt to asset ratios, such as 0% to 30%, the main advantage is that they would incur less interest expense and also have greater strategic flexibility. If hypothetically liquidated, a company with more assets than debt could still pay off its financial obligations using the proceeds from the sale. The accounts receivable turnover will be calculated by dividing the net credits by the average accounts receivable.
Organization

Christopher should seek immediate action towards remedying the situation, such as hiring a financial advisor to help. If he doesn’t do anything to alter the trajectory of his company’s finances, it will go bankrupt within the next couple of years. With both numbers inserted into https://www.bookstime.com/articles/ecommerce-bookkeeping the debt to asset ratio equation, he solves. Debt ratio on its own doesn’t provide insights into a company’s operating income or its ability to service its debt. Debt ratio provides insights into a company’s capital structure by showcasing the balance between debt and equity.
Debt to asset ratio formula
- As you can see, the values of the debt-to-asset ratio are entirely different.
- A debt ratio of zero would indicate that the firm does not finance increased operations through borrowing at all, which limits the total return that can be realized and passed on to shareholders.
- On the surface, the risk from leverage is identical, but in reality, the second company is riskier.
- Financial data providers calculate it using only long-term and short-term debt (including current portions of long-term debt), excluding liabilities such as accounts payable, negative goodwill, and others.
- Last, the debt ratio is a constant indicator of a company’s financial standing at a certain moment in time.
- Typically, a debt ratio of 0.4 or below would be considered better than a debt ratio of 0.6 and higher.
- Depending on your lender, you might need to provide supporting documentation such as tax returns or bank statements demonstrating consistent income deposits to validate your income.
Because companies receive better reactions to lower debt ratios, they can borrow more money. When evaluating a business, the debt to asset ratio states how much of your expenses were paid for with credit, loans, or any other form of debt. This number demonstrates the financial status of a company and can measure its growth over time by showing the minimization of the debt to asset ratio over the years.
What is your current financial priority?
As is often the case, comparisons of the debt ratio among different companies are meaningful only if the companies are similar, e.g. of the same industry, with a similar revenue model, etc. When calculated over several years, this leverage ratio can show a company’s use of leverage as a function of time. For example, a ratio that drops 0.1% every year for ten years would show that as a company ages, it reduces its use of leverage.
- Apple has a debt to asset ratio of 31.43, compared to an 11.47% for Microsoft, and a 2.57% for Tesla.
- Ted’s bank would take this into consideration during his loan application process.
- While this could indicate aggressive financial practices to seize growth opportunities, it might also mean a higher risk of financial distress, especially if cash flows become inconsistent.
- Contrarily, if the company’s assets yield low returns, a low debt ratio does not automatically translate into profitability.
- In other words, it shows what percentage of assets is funded by borrowing compared with the percentage of resources that are funded by the investors.
- Having a poor debt to asset ratio lowers the chances that you’ll receive a good interest rate or a loan at all in the future.
Example of Long-Term Debt to Assets Ratio
Cesar was being recruited by a competitor due to his success at his current company in getting several new patents. Or due to his success at his current company in getting several new patents. Dave, a self-taught investor, empowers investors to start investing by demystifying the stock market. After all, we get a pretty good idea of how the ratio works and what to look for when calculating the debt-to-asset ratio. Unfortunately, the financial standing of Lucky Charms seems to be progressively getting worse.

Investors’ returns are magnified when the firm earns more on the investments it makes with borrowed money than it pays in interest. Because a ratio greater than 1 also indicates that a large debt to asset ratio portion of your company’s assets are funded with debt, it raises a red flag instantly. It also puts your company at a higher risk for defaulting on those loans should your cash flow drop.
On the other hand, a lower debt-to-total-assets ratio may mean that the company is better off financially and will be able to generate more income on its assets. Applying this, as an example, a company with $2 million in total assets and $500,000 in total liabilities would have a debt ratio of 25%. Another consideration is that companies with low debt maintain the option of raising debt capital in the future under more favourable terms. A steadily rising D/E ratio may make it harder for a company to obtain financing in the future. The growing reliance on debt could eventually lead to difficulties in servicing the company’s current loan obligations. Very high D/E ratios may eventually result in a loan default or bankruptcy.
A company’s total debt-to-total assets ratio is specific to that company’s size, industry, sector, and capitalization strategy. For example, start-up tech companies are often more reliant on private investors and will have lower total debt-to-total-asset calculations. However, more secure, stable companies may find it easier to secure loans from banks and have higher ratios. In general, a ratio around 0.3 to 0.6 is where many investors will feel comfortable, though a company’s specific situation may yield different results. Once you have your total monthly debt payments and gross monthly income, divide the former by the latter to arrive at your DTI ratio. This calculation yields a percentage representing the proportion of your income that goes toward servicing debt.
- These loans for individuals and businesses can bring together all of your debt into a single, predictable monthly payment.
- Understanding the result of the equation is done by examining it for being high or low.
- In a consensus rule, everyone’s opinion is heard and a solution is created that goes with the opinions that were heard.
- The business owner or financial manager can gain a lot of insight into the firm’s financial leverage through trend analysis.
- It represents the proportion (or the percentage of) assets that are financed by interest bearing liabilities, as opposed to being funded by suppliers or shareholders.